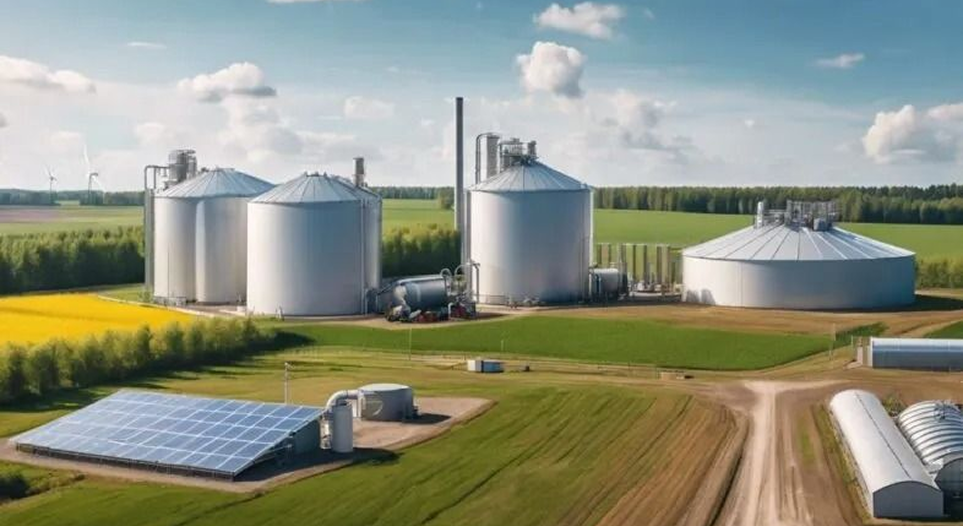

Biomass / Waste-to-Energy Solutions are renewable energy solutions that convert organic waste such as agricultural residues, wood, municipal waste, or food waste into energy in the form of electricity, heat, or fuel. Biomass is processed through technologies such as combustion, gasification, or biogas, while solid waste is processed through modern incineration or anaerobic digestion. These solutions not only produce clean energy that reduces reliance on fossil fuels, but also help reduce waste volume, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and support the concept of a circular economy by utilizing waste as a valuable resource.
In other words, Biomass / Waste-to-Energy Solutions is a transformative concept that combines energy innovation with environmental management. It exists as a response to two major challenges in the modern world: the need for sustainable energy and waste management. If widely implemented, this solution has great potential to become a key pillar in realizing a clean, safe, and environmentally friendly energy future.
KEY COMPONENTS OF BIOMASS / WASTE-TO-ENERGY
MAIN BENEFITS
This solution can reduce the volume of waste piled up in landfills (TPA) while also mitigating negative impacts such as air pollution, odors, and groundwater contamination. The waste-to-energy process also helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, as organic waste, which typically produces methane during decomposition, can be converted into more environmentally friendly biogas or electricity.

Frequently Asked Questions
Biomass and Waste-to-Energy Solutions are technologies that convert organic materials or waste into usable energy, such as electricity, heat, or biofuels. This process reduces landfill waste while providing renewable and sustainable energy sources.
The key benefits include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, lowering reliance on fossil fuels, managing waste more efficiently, and generating clean energy. These solutions also support circular economy practices by turning waste into valuable resources.
They can be applied in power generation plants, industrial operations, and community energy projects. On a smaller scale, biomass heating systems can be used in homes or businesses, while large-scale facilities can convert municipal or agricultural waste into electricity and heat.